all configurations on | 2.5KB | 1.03KB | 852B | 8B | | main loop mode,
all configurations off(3) | 616B | 600B | 180B | 0B | | react mode,
all configurations on | 2.52KB | 1.03KB | 852B | 8B | | react mode,
all configurations off(3) | 608B | 600B | 180B | 0B | > 1: include built-in `help` command. > > 2: include `input buffer`(default 128Bytes) and `hisroty record buffer`(defaut 650Bytes(5*(128+2))) > > 3: except `CONFIG_SHELL_CMD_BUILTIN_HELP`. --- ## Hot Key Bind nano-shell has internally bound these hotkeys: | HOT KEY | ASCII/ANSI-Escape Code
(Xterm, VT100) | Function | |---------|------------------------|----------| | Ctrl-A | 1 | Home
Move curosr to the start of line.| | Ctrl-E | 5 | End
Move curosr to the end of line.| | Ctrl-P | 16 | Up arrow(-->)
Move cursor right one char.| | Ctrl-N | 14 | Down arrow(-->)
Move cursor right one char.| | Ctrl-B | 2 | Left arrow(<--)
Move cursor left one char.| | Ctrl-F | 6 | Right arrow(-->)
Move cursor right one char.| | Ctrl-D | 4 | Delete
Delete the character under the cursor.| | Ctrl-K | 11 | Erase forward
Clears all characters from the cursor position to the end of the line.| | Ctrl-U | 21 | Erase backword
Clears all characters from the cursor position to the start of the line..| | Ctrl-C | 3 | Kill the line.| | Home | Esc[H | Move curosr to the beginning of line.| | End | Esc[F | Move curosr to the end of line.| | Up Arrow | Esc[A | Get the previous history. | | Down Arrow | Esc[B | Get the next history. | | Left Arrow | Esc[D | Left arrow(<--)
Move cursor left one char. | | Right Arrow | Esc[C | Right arrow(-->)
Move cursor right one char.| | Delete | Esc[3~ | Delete the character under the cursor.| --- ## Add Your Command ### HOW: Commands are added to nano-shell by creating a new command structure. This is done by first including `command/command.h`, then using the `NANO_SHELL_ADD_CMD()` macro to fill in a `shell_cmd_t` struct. ``` c NANO_SHELL_ADD_CMD(_name, _func, _brief, _help) ``` `_name`: name of the command. Note: **THIS IS NOT** a string. `_func`: function pointer: `(*cmd)(const shell_cmd_t *, int, int, char *const[])`. `_brief`: brief summaries of the command. This is a string. `_help`: detailed help information of the command. This is a string. Commands with sub-commands can easily be created with a combination of `NANO_SHELL_DEFINE_SUBCMDS`, `NANO_SHELL_SUBCMD_ENTRY` and `NANO_SHELL_ADD_CMD`. See examples for more details. ### Example 1: Simple command: ```c int _do_demo(const shell_cmd_t *pcmd, int argc, char *const argv[]) { for (int i=0; i
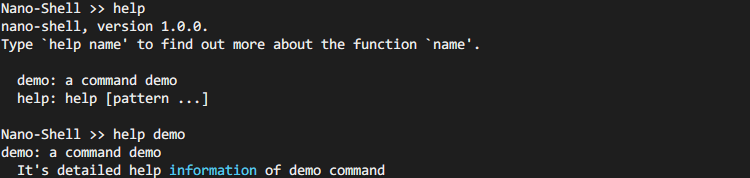 ### Example 2: Command with sub-commands:
It is possible to create commands with sub-commands. More nested command can also be created.
```c
/* Create a bunch of commands to be run as a demo */
int _top_command_fallback_fct(const shell_cmd_t* pCmdt, int argc, char* const argv[])
{
if(argc > 1) {
shell_printf(" '%s' is not a subcommand of %s\r\n", argv[1], argv[0]);
}
else {
shell_printf(" Hey, there is subcommands here, type '%s help' for more info\r\n", argv[0]);
}
return 0;
}
int _do_subcommand1(const shell_cmd_t* pCmdt, int argc, char* const argv[]) {
shell_puts(" This is sub-command 1\r\n");
return 0;
}
int _do_subsubcommand1(const shell_cmd_t* pCmdt, int argc, char* const argv[]) {
shell_puts(" This is sub-sub-command 1\r\n");
return 0;
}
int _do_subsubcommand2(const shell_cmd_t* pCmdt, int argc, char* const argv[]) {
shell_puts(" This is sub-sub-command 2\r\n");
return 0;
}
// Sub-Sub commands group
NANO_SHELL_DEFINE_SUBCMDS(subcommand2_group,
NULL,
NANO_SHELL_SUBCMD_ENTRY(subsubcommand1,
_do_subsubcommand1,
"first sub-sub-command",
""),
NANO_SHELL_SUBCMD_ENTRY(subsubcommand2,
_do_subsubcommand2,
"second sub-sub-command",
""));
// Sub commands group
NANO_SHELL_DEFINE_SUBCMDS(top_command_group,
_top_command_fallback_fct,
NANO_SHELL_SUBCMD_ENTRY(subcommand1,
_do_subcommand1,
"first subcommand",
""),
NANO_SHELL_SUBCMD_ENTRY(subcommand2,
NANO_SHELL_SUBCMDS_FCT(subcommand2_group),
"second subcommand with sub-sub commands",
""));
// Command with sub commands
NANO_SHELL_ADD_CMD(top_command,
NANO_SHELL_SUBCMDS_FCT(top_command_group),
"A command with subcommand",
" This command have 2 sub-commands and one sub-sub-command\r\n");
```
In a terminal, you get:
### Example 2: Command with sub-commands:
It is possible to create commands with sub-commands. More nested command can also be created.
```c
/* Create a bunch of commands to be run as a demo */
int _top_command_fallback_fct(const shell_cmd_t* pCmdt, int argc, char* const argv[])
{
if(argc > 1) {
shell_printf(" '%s' is not a subcommand of %s\r\n", argv[1], argv[0]);
}
else {
shell_printf(" Hey, there is subcommands here, type '%s help' for more info\r\n", argv[0]);
}
return 0;
}
int _do_subcommand1(const shell_cmd_t* pCmdt, int argc, char* const argv[]) {
shell_puts(" This is sub-command 1\r\n");
return 0;
}
int _do_subsubcommand1(const shell_cmd_t* pCmdt, int argc, char* const argv[]) {
shell_puts(" This is sub-sub-command 1\r\n");
return 0;
}
int _do_subsubcommand2(const shell_cmd_t* pCmdt, int argc, char* const argv[]) {
shell_puts(" This is sub-sub-command 2\r\n");
return 0;
}
// Sub-Sub commands group
NANO_SHELL_DEFINE_SUBCMDS(subcommand2_group,
NULL,
NANO_SHELL_SUBCMD_ENTRY(subsubcommand1,
_do_subsubcommand1,
"first sub-sub-command",
""),
NANO_SHELL_SUBCMD_ENTRY(subsubcommand2,
_do_subsubcommand2,
"second sub-sub-command",
""));
// Sub commands group
NANO_SHELL_DEFINE_SUBCMDS(top_command_group,
_top_command_fallback_fct,
NANO_SHELL_SUBCMD_ENTRY(subcommand1,
_do_subcommand1,
"first subcommand",
""),
NANO_SHELL_SUBCMD_ENTRY(subcommand2,
NANO_SHELL_SUBCMDS_FCT(subcommand2_group),
"second subcommand with sub-sub commands",
""));
// Command with sub commands
NANO_SHELL_ADD_CMD(top_command,
NANO_SHELL_SUBCMDS_FCT(top_command_group),
"A command with subcommand",
" This command have 2 sub-commands and one sub-sub-command\r\n");
```
In a terminal, you get:
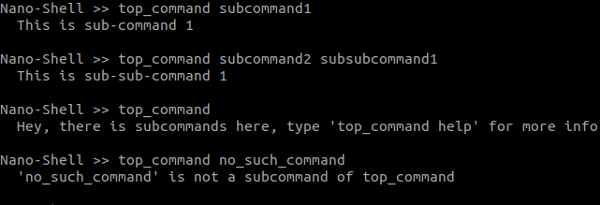 ---
## Configuring
@file: [`shell_config.h`](/shell_config.h)
### readline configurations:
- CONFIG_SHELL_INPUT_BUFFSIZE (127U)
- default: `(127U)`
- config the command line input buffer size (in byte).
- CONFIG_SHELL_LINE_EDITING
- default: `1(enabled)`
- set this to `0` will disable command line editing.
- CONFIG_SHELL_KEY_SEQ_BIND
- default: `1(enabled)`
- set this to `0` will disable ANSI-Escape-Sequence. nano-shell will not be able to detect Home/End/Delete/Arrow keys. Doesn't affect Ctrl-P, Ctrl-N, etc...
- CONFIG_SHELL_MULTI_LINE
- default: `1(enabled)`
- use Backslash('\\') for line continuation when enabled, set this to `0` will disable line continuation.
- line continuation example:
---
## Configuring
@file: [`shell_config.h`](/shell_config.h)
### readline configurations:
- CONFIG_SHELL_INPUT_BUFFSIZE (127U)
- default: `(127U)`
- config the command line input buffer size (in byte).
- CONFIG_SHELL_LINE_EDITING
- default: `1(enabled)`
- set this to `0` will disable command line editing.
- CONFIG_SHELL_KEY_SEQ_BIND
- default: `1(enabled)`
- set this to `0` will disable ANSI-Escape-Sequence. nano-shell will not be able to detect Home/End/Delete/Arrow keys. Doesn't affect Ctrl-P, Ctrl-N, etc...
- CONFIG_SHELL_MULTI_LINE
- default: `1(enabled)`
- use Backslash('\\') for line continuation when enabled, set this to `0` will disable line continuation.
- line continuation example:
- CONFIG_SHELL_HIST_MIN_RECORD - default: `(5U)` - set this to `0` will disable history record. - nano-shell will take `CONFIG_SHELL_HIST_MIN_RECORD*(2+CONFIG_SHELL_INPUT_BUFFSIZE)` bytes to record **At Least** `CONFIG_SHELL_HIST_MIN_RECORD` histroys. The max history records depends on the average length of the input. ### command configurations: - CONFIG_SHELL_CMD_BRIEF_USAGE - default: `1(enabled)` - command structure `shell_cmd_t` has a pointer point to "brief usage information of the command", set this to `0` will remove it. - CONFIG_SHELL_CMD_LONG_HELP - default: `1(enabled)` - command structure `shell_cmd_t` has a pointer point to "detailed help information of the command", set this to `0` will remove it. - CONFIG_SHELL_CMD_BUILTIN_HELP - default: `1(enabled)` - nano-shell provides a built-in `help` command, set this to `0` will remove the deault `help` command. - CONFIG_SHELL_CMD_MAX_ARGC - default: `(10U)` - config the max number of arguments, must be no less than 1. ### shell configurations: - CONFIG_SHELL_PROMPT - default: `"Nano-Shell >> "` - config the shell promot that will displayed at the start of line. If you don't need it, set this to `NULL` or `""`. ### shell io configurations: - CONFIG_SHELL_PRINTF_BUFFER_SIZE - default: `(128U)` - config the buffer size of `shell_printf()`. --- ## Porting nano-shell to your project ### 1. add nano-shell root path to your project include path. ### 2. implement these functions([`@file shell_io.h`](/shell_io/shell_io.h)) in your project: this file may help: [`/shell_io/shell_io.c`](/shell_io/shell_io.c). ```c /** * @brief send a chararcter... * */ extern void shell_putc(char ch); /** * @brief send string... * */ extern void shell_puts(const char *str); /** * @brief printf() for nano-shell * */ extern int shell_printf(const char *format, ...) __attribute__((format(printf, 1, 2))); /** * @brief: Get next character available from stream. * * @param ch: Return the character in `ch` if there was... * @return: Result is non-zero if there was a character, or 0 if there wasn't. * */ extern int shell_getc(char *ch); ``` Note: - `int shell_getc(char *ch)` is **NOT USED** in `
 ## Contents
- [Hot Key Bind](#hot-key-bind)
- [Add Your Command](#add-your-command)
- [HOW:](#how)
- [Example:](#example)
- [Configuring](#configuring)
- [readline configurations:](#readline-configurations)
- [command configurations:](#command-configurations)
- [shell configurations:](#shell-configurations)
- [shell io configurations:](#shell-io-configurations)
- [Porting nano-shell to your project](#porting-nano-shell-to-your-project)
---
Nano-Shell is a light but powerful shell designed for embedded systems.
- with or without an operating system;
- `
## Contents
- [Hot Key Bind](#hot-key-bind)
- [Add Your Command](#add-your-command)
- [HOW:](#how)
- [Example:](#example)
- [Configuring](#configuring)
- [readline configurations:](#readline-configurations)
- [command configurations:](#command-configurations)
- [shell configurations:](#shell-configurations)
- [shell io configurations:](#shell-io-configurations)
- [Porting nano-shell to your project](#porting-nano-shell-to-your-project)
---
Nano-Shell is a light but powerful shell designed for embedded systems.
- with or without an operating system;
- `